There are various methods by which to evaluate zipper strength. The basic strength can be determined based on the results of the following inspection methods, from which overall strength appropriate for respective uses can be judged. (Based on JIS-S3015 and ASTM D2061)
Product Testing Methods
Seeking corporate value of higher significance
Ensuring the Quality and Durability of our Products
Zipper Testing Methods
Tensile Testing Machine Conditions
Tensile Speed: 300 mm/min, Clamp Width: 25 mm
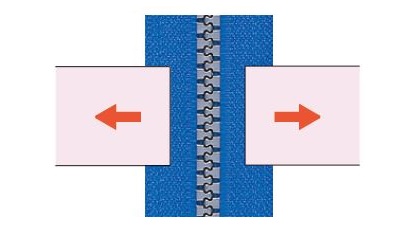
Chain crosswise strength (per 2.5cm)
An engaged zipper chain is pulled crosswise as shown at a constant speed.
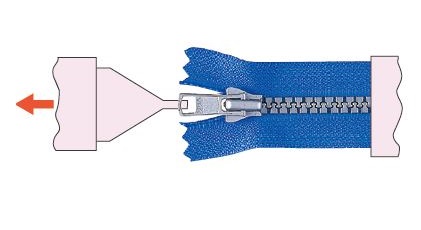
Top stop holding strength
The lower part of an engaged zipper is held securely, then the slider pulled to the top is pulled further up.

Bottom stop holding strength
The slider is pulled down to the bottom stop, and each side of the chain is pulled outwards in opposite directions.
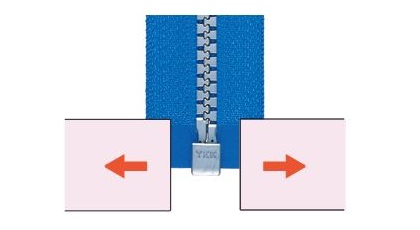
Separating unit crosswise strength
The slider lock is engaged in the middle of a chain, then each side of the chain is pulled outwards in opposite directions.

Slider lock strength
The slider lock is engaged in the middle of a chain, then each side of the chain is pulled outwards in opposite directions.
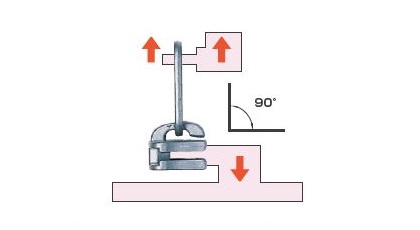
Slider tab pull off strength (90 degree)
Tension force is applied to both the puller and the bottom of the body of an assembled slider.
In addition to the 90°angle shown, a 45°angle is also tested.
(Tensile Testing Machine Speed: 100 mm/min)
Plastic Hardware Testing Methods
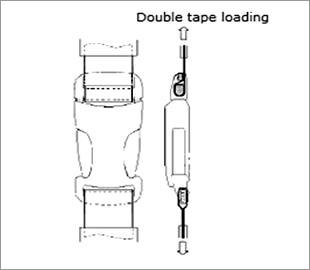
Buckle tensile strength test
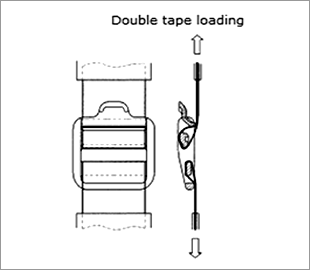
Strap adjuster tensile strength test
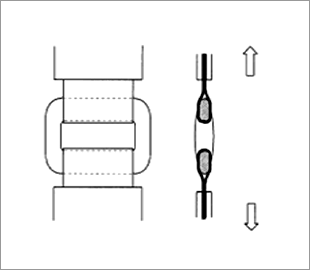
Wedge adjuster tensile strength test
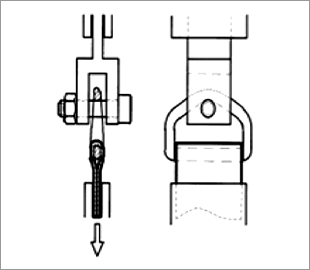
D-Ring tensile strength test
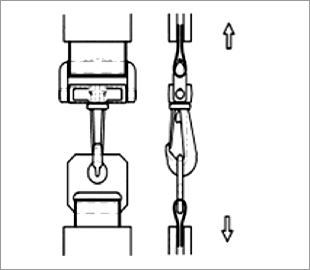
Snap hook tensile strength test
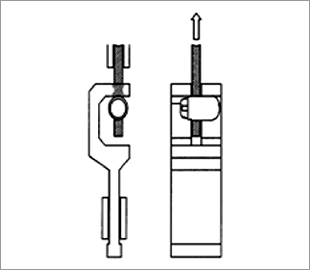
Cord stopper tensile strength test
Hook & Loop Testing Methods
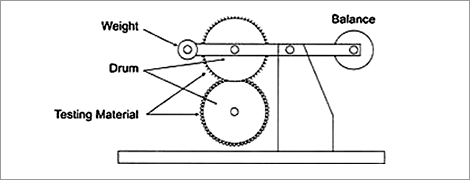
Durability Test
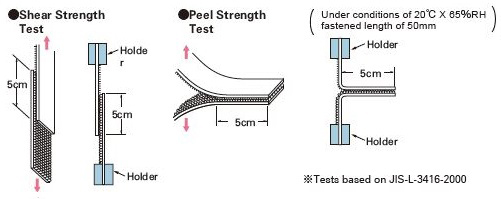
Strength of adhesion
Snap and Button Testing Method

Direct Pull Strength
Tack Button
A force is applied diametrically until the tack button separates from the tack or the fabric is torn. The force at separation is reported as the holding strength.

Peel Off Strength
Rivet & Burr, Snap, Eyelet & Washer
The lower part of an engaged zipper is held securely, then the slider pulled to the top is pulled further up.

Direct Pull Strength
SNAPET®
The slider is pulled down to the bottom stop, and each side of the chain is pulled outwards in opposite directions.

Lateral Strength
Hook & Eye
A force is applied diametrically until the tack button separates from the tack or the fabric is torn. The force at separation is reported as the holding strength.

Slippage Strength
SOFIX®
The lower part of an engaged zipper is held securely, then the slider pulled to the top is pulled further up.
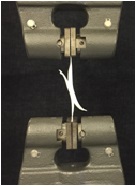
Lateral Holding Strength
SOFIX®
The slider is pulled down to the bottom stop, and each side of the chain is pulled outwards in opposite directions.
